
Meanwhile, there are several studies that show that with an optimal vitamin D level in the blood, the risk of contracting COVID-19 can be massively reduced or, in the case of a COVID-19 disease, its severity and the course of the disease can be greatly alleviated. A study from Spain shows: Vitamin D reduces the risk of admission to an intensive care unit by 97%!
Supporting the immune system
The Corona virus continues to keep the world on tenterhooks, with diligent research for a vaccine and protective measures that are very impactful on social life and the economy. With all the efforts, it seems to me, we almost forget that humans are equipped with an incredibly complex and ingenious immune system! If we can support this system in its function optimally, we would be well equipped in the fight against the dreaded virus. A relatively simple and inexpensive option is supplementation with vitamin D. The human body uses vitamin D for countless purposes. This is urgently needed by the human body for countless important functions, including support of the immune system.
Sun vitamin
Supplementation with vitamin D is becoming an issue again in the “dark season” that is beginning in our latitudes anyway. The human body can produce vitamin D itself with the help of sunlight. When we are in the sun, vitamin D3 is formed in the skin, which is subsequently converted to vitamin D. However, the intensity of light and thus the formation of vitamin D3 in the skin are influenced by many factors (e.g. position of the sun, altitude above sea level, weather, use of sunscreens, etc.). In the winter half-year (October to March) in this country there is no sufficient amount of UV-B rays, which are needed for vitamin D synthesis in the skin! It can therefore be assumed that about 70% of the Swiss population has a vitamin D deficiency. This figure is given by the Swiss government, but in reality the value is much higher.
How does vitamin D work against viruses?
It is known that vitamin D can reduce the risk of infection; on the one hand through the release of cathelicidins (antimicrobial peptides and part of the innate immune response) and on the other hand through defense mechanisms that can reduce virus replication. Furthermore, vitamin D lowers the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines. These cause inflammation, damage the mucous membrane of the lungs and can trigger pneumonia. This argues for the prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19 infection.
Vitamin D in the fight against COVID-19: Studies
I am happy to inform you here about recommended studies on the subject:
- COVID-19 positivity rates in relation to vitamin D levels in the blood:
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.02392
The results of this study of over 190,000 people from the US show an inverse relationship between 25(OH)D levels (blood vitamin D levels) and COVID-19 positivity. Measured across the entire population (across all latitudes, races and ethnicities, genders, and ages), those who had low 25(OH)D levels of less than 20 ng/ml had a 54% higher positivity rate than those who had blood levels of 30-34 ng/ml. The risk of COVID-19 positivity decreased further until serum levels reached 55 ng/ml. This is not surprising given the already established inverse relationship between risk for respiratory viral pathogens and 25(OH)D levels. Thus, vitamin D supplementation may reduce the likelihood of respiratory infections, especially in people with vitamin D deficiency.
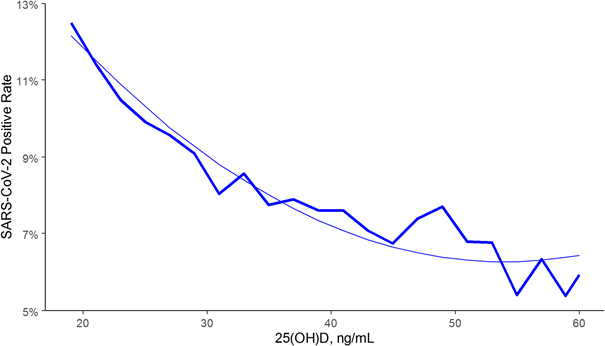
Explanation: In individuals with low vitamin D levels (left margin), up to 13% had a positive corona test. In people with high vitamin D levels (right margin), less than 7% did.
Vitamin D levels (25(OH)D are reported here in ng/ml. Depending on the laboratory, values are also given in nmol/l (more common in Switzerland). Values in ng/ml x 2.5 give the values in nmol/l. I recommend values between 150-200 nmol/l, which corresponds to the values at the right margin.
- The positive influence of vitamin D on hospitalized patients with COVID-19; a study collected at the Reina Sofia University Hospital in Spain:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7456194/
This was a randomized controlled trial of hospitalized COVID-19 patients at the Reina Sofia University Hospital, in Cordoba, Spain. All 76 patients were hospitalized for severe COVID-19 infection. Thus, these were not mild or moderate disease courses. The intervention group consisted of 50 patients and the control group consisted of 26 patients. Both groups, of course, received the best available treatment at the time. The intervention group also received vitamin D in the form of calcifediol, while the control group received no placebo. Calcifediol (also calcidiol or 25-hydroxyvitamin D) is a hormone precursor to vitamin D. It is formed in the liver from cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), and is a storage form. The reason for administering this type of vitamin D was that the conversion of the usual supplement type to calcifediol takes about seven days, and the patients mentioned should be able to benefit from a faster-acting form because of their disease. They received the vitamin D in very high doses and the results were astounding: of the 50 patients in the intervention group treated with calcifediol, only one had to be referred to the intensive care unit (2%), while of the patients in the control group, this was the case in 13 patients (50%). In the statistically adjusted results, vitamin D reduced the probability of ICU admission by 97%! As for mortality, two patients in the control group died, but no patient in the intervention group who received the vitamin D died. The prevention of deaths can be expected to be of a similar magnitude to the decrease in the need for intensive care. Vitamin D also appears to decrease the need for mechanical ventilation in the ICU.
- The interested reader can find more studies here:
https://covid.us.org/vitamin-d/
Taking a vitamin D supplement has tremendous benefits
In my opinion, there is now sufficient evidence that vitamin D treatment should be a standard of care for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Also, especially in the coming winter months and with “rising case rates,” vitamin D supplementation should simply be recommended to all individuals, especially those at increased risk, such as the elderly.
Implications for the pandemic
Vitamin D reduces the risks of COVID-19: the risk of getting an infection in the first place, the risk of going through a severe course, the risk of needing hospitalization, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation, and the risk of dying from COVID-19.
My dosing recommendations:
Optimally, one determines his or her vitamin D status with a blood draw: measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D for short) in the blood serum. 25(OH)D is expressed in units of nmol/l or ng/ml, depending on the laboratory (to convert nmol/l to ng/ml, divide the value by 2.5). The 25(OH)D level should be between 150-200 nmol/l. To achieve this goal, a daily dose of about 4000 IU or 100 micrograms of vitamin D is needed in most cases. In winter, 5000-6000 IU per day can be taken without any problems, while in summer it can then be reduced to 3000 IU. To maintain the vitamin D level in the blood (when it is already between 150-200 nmol/l), about 2000 IU are needed daily.
